How to Install Android in VirtualBox
If you want to use Android on your computer but don't actually want to use your whole computer for the task, using a virtual machine like VirtualBox is the best option and it's quite easy.




















How to Create a Virtual Machine for Android
Go ahead and fire up VirtualBox, then click the “New” button to creation a new virtual machine.

Name the virtual machine whatever you’d like (I’m using “Android” because that just kind of makes sense?), then select “Linux” as the type and “Linux 2.6 / 3.x / 4.x (32-bit)” as the version. Click Next.

For memory, I’d give it 2048MB, especially if you’re using a 32-bit build of Android (it can’t handle anything more). If you’re using a 64-bit build, feel free to use as much as you want. Once you’ve set the amount, click Next.

Click “Create” to start building your virtual machine. For hard disk type, leave it set as VDI.

Leave the hard disk size set as Dynamically Allocated, which will allow the virtual hard disk to grow as needed.
On the next step, you can choose how much storage you’d like to top the virtual machine out at—even though it will dynamically resize, it won’t be allowed to grow past the size you define here. Choose whatever size will work best for your system. I’m leaving this at 8GB.

Finally, click the Create button.
Poof! Just like that, your new virtual machine is ready to use.
How to Install Android in a Virtual Machine
With your machine all set up, highlight it and click on Start at the top.

When the machine starts up, point it to the Android ISO you downloaded. It should allow you to choose this as soon as you fire it up, but if not, click on Devices > Optical Drives > Choose Disk Image and select your Android ISO. Then use Machine > Reset to restart the virtual machine.

NOTE: When you click on the VirtualBox window, it will automatically capture the mouse and keyboard. To release the mouse and keyboard, just tap the right Ctrl key on the keyboard.
Once the virtual machine loads the ISO, use the keyboard to scroll down to “Install ” and press enter. This will start the Android installer.

Choose “Create/Modify” partitions. On the GPT screen, just choose “No.”

On the disk utility screen, select “New.”

Create a Primary disk and allow it to use the entire virtual hard disk space you chose earlier. In this case, it’s 8GB. This should be selected by default.

Hit Enter on the “Bootable” option to make the partition bootable, then choose “Write.” Tap Enter.

You will need to type “yes” and tap Enter on the following screen to verify you want to write the partition table to the disk.

Once it’s finished, highlight the Quit option and tap Enter.

Select the partition you just created to install Android on and tap Enter.

Select “ext4” to format the partition.
Highlight Yes and tap enter on the next screen to verify.

Choose “Yes” to install the GRUB bootloader.

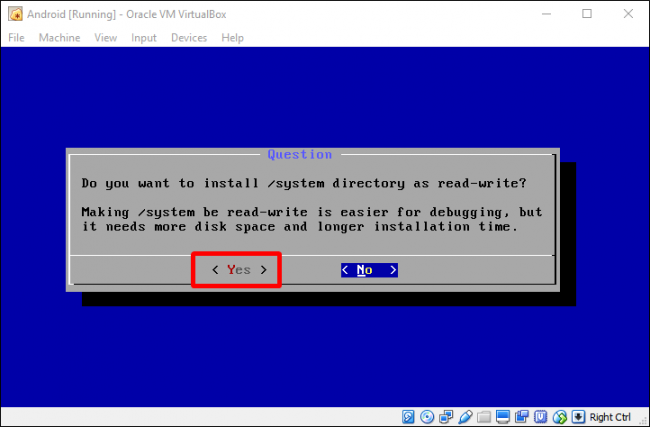
Choose “Yes” to make the /system folder re-writable.

Once everything is finished, you can choose to reboot into Android or reset. Feel free to do either thing right here, but don’t forget to unmount the ISO file first. Otherwise it’ll just boot right back into the installer!

Using Android in VirtualBox
From here, the setup process is pretty cut and dry—you’ll set this thing up just like any other Android device, save for one exception: you won’t turn on Wi-Fi. The virtual machine will use your PC’s connection.

So yeah, just sign in and finish the set up. You’re ready to play!

However this isn't the fastest way to run android on your computer- bluestacks is faster but it will do good if you want to run only an app or two. Android-x86 provides access to a complete Android system in a virtual machine. It’s a great way to get more familiar with a standard Android system or just experiment with it.


Comments
Post a Comment